Introduction
Lean manufacturing, a widely acclaimed management philosophy, is playing an increasingly vital role in various industries worldwide. This approach, which emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and streamlined processes, has shown to be particularly beneficial in the burgeoning agriculture and cultivation sectors. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of lean manufacturing in cultivation and discuss how its principles can be applied to optimize production processes, ensuring both efficiency and sustainability.
The agriculture industry has undergone rapid growth and transformation in recent years, fueled by the evolution of technology, shifting consumer preferences, and increasing global demand for various products. As the sales environment becomes more competitive, cultivators are faced with the challenge of scaling their operations while maintaining high standards of quality and consistency and lowering costs. The adoption of lean manufacturing principles offers a solution to these challenges, enabling businesses to remain competitive and environmentally conscious in an industry characterized by rigorous regulations and shifting consumer preferences.
Background of Lean Manufacturing
Origin of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing, originating in the automotive industry by Toyota Motor Corporation in the 1930s-1940s, focuses on waste elimination and process efficiency. The approach has been widely adopted by organizations across industries, leading to enhanced productivity, quality, and cost reduction.
Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is based on these core principles:
- Value: Define value from the customer's perspective to understand the desired outcome.
- Value Stream: Mapping the value stream helps visualize the production process and identify waste.
- Flow: A smooth and continuous flow of work increases efficiency and reduces delays.
- Pull: A pull-based system, driven by customer demand, reduces inventory waste and optimizes resource allocation.
- Perfection: Striving for continuous improvement (Kaizen) encourages ongoing waste elimination and process enhancement.
Benefits of Adopting Lean Manufacturing Practices
Lean manufacturing offers significant benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved Productivity: Streamlined processes result in higher output and efficiency.
- Reduced Costs: Waste reduction and effective resource allocation lead to cost savings.
- Higher Quality: Standardized processes and continuous improvement ensure consistent, high-quality products.
- Increased Flexibility: Lean manufacturing helps organizations adapt to changes in demand and market conditions.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Involving employees in continuous improvement and waste reduction boosts satisfaction, motivation, and retention.
The Cultivation Industry
Current Challenges Faced by the Industry
The cultivation industry is confronted with multiple challenges as it strives to meet the demand for quality product in an increasingly competitive and lower margin environment.
- Resource Management: Efficiently using resources such as water, energy, fertilizer, and materials is crucial for sustainable cultivation practices.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing the environmental footprint of cultivation operations, including minimizing waste, lowering emissions, reducing net water use, and promoting biodiversity, is increasingly important.
- Regulations and Compliance: Navigating complex and evolving regulations while maintaining high product quality and safety standards is an ongoing challenge.
- Labor and Workforce: Retaining skilled workers and optimizing labor productivity is essential for the industry's success.
- Market Fluctuations: Managing the impact of market fluctuations, such as changing consumer preferences and economic conditions, requires adaptability and resilience.
The Need for Efficiency and Sustainability in Cultivation
To overcome these challenges, the cultivation industry must continuously innovate and optimize its practices to remain competitive and sustainable. Adopting lean manufacturing principles can help cultivators improve their operational efficiency, minimize waste, and adapt to changing market conditions. Key areas to focus on in cultivation include:
-
Facility design and logistics: Using math to determine the most efficient allocation of space and room sizes for a given facility is critical. Two key factors:
- Allocation of relative flowering, veg, and support areas.
- Division of growth areas into room numbers and sizes that eliminate downtime. The veg should be at the minimum size that allows the flower rooms to be refilled continuously. The dry area should be the minimum size as to accommodate each harvest without downtime.
-
Cultivar selection: Selecting high-yielding and disease resistant strains that are well-suited to the growing conditions. Use data-driven insights and KPIs to refine cultivar library, such as
- Yield: grams / ft2 / day. For example, a strain that yield 90g/ft2 in a 63 day window would be 1.43 g/ft2/day.
- Revenue: factoring in sales price per gram to calculate $ / ft2 / day. To continue the previous example, if the wholesale value of that strain is $1600, that would equal $5/ft2/day.
-
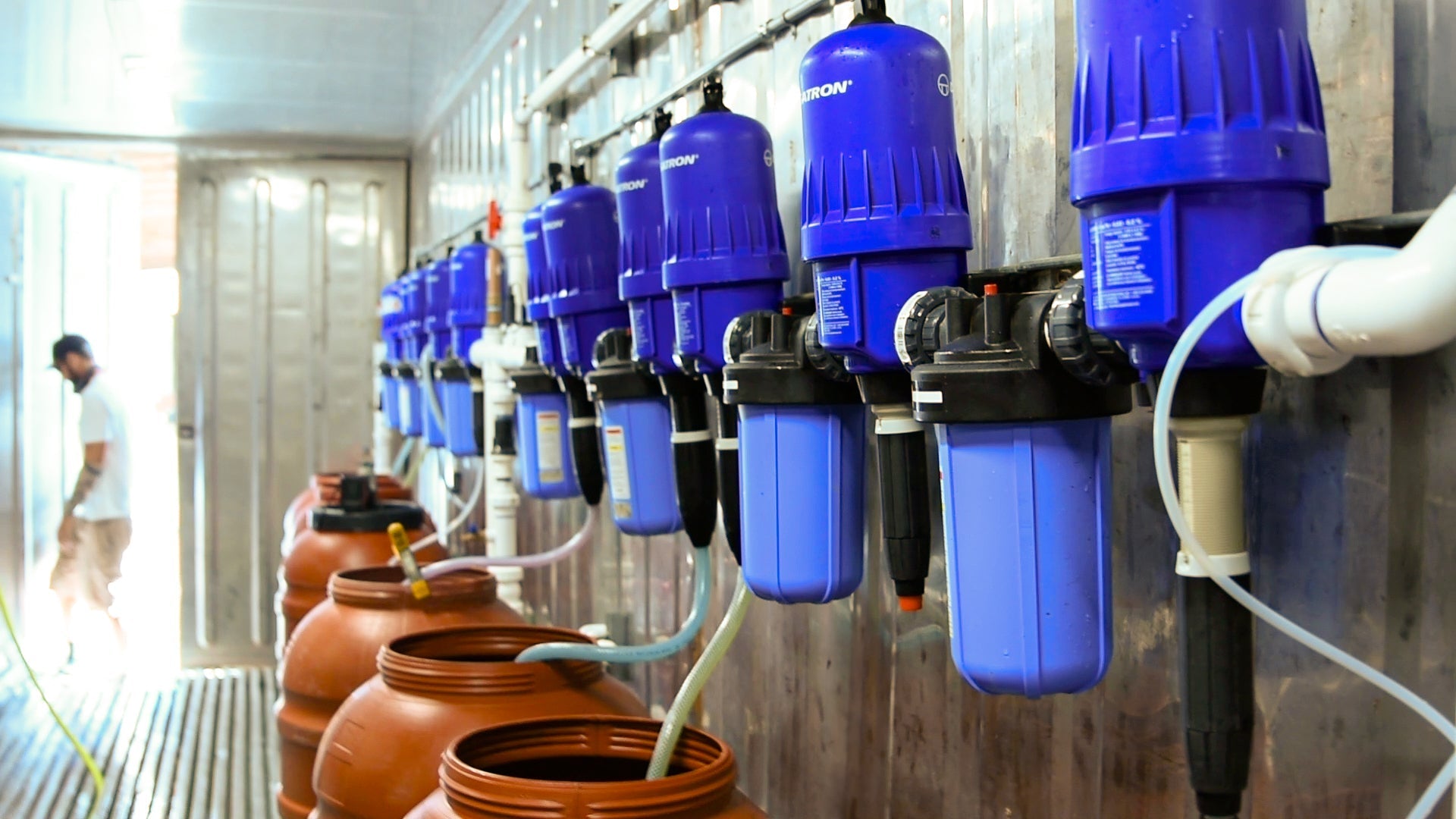
Substrate and nutrient management: Use substrate that optimizes water characteristics and nutrient retention while minimizing the risk of diseases and pests, coco coir and rockwool being the current standard for hydroponics.
-
Irrigation and water management:
- Use precision drip irrigation systems with high uniformity and carefully manage the percentage of runoff.
- Use an integrated nutrient system that provides all they key elements in the correct quantities and ratios required for vigorous plant growth.
- Use water reclamation equipment such as capturing and treating condensate from HVAC equipment for reuse, as well as more advanced systems such as the Tru-Zero Zero Water Discharge System
-
Lighting and environmental control:
- Optimize lighting spectrum and intensity with high-efficiency LED lights. Current LED lights offer photon efficiencies of 2.6 umol/watt and above.
- Accurate and reliable controls to create optimal environmental conditions for growth while reducing waste from losses due to poor growth or disease.
-
Plant Work: As labor costs become a higher percentage of cultivation cost of goods (COGs), practices that reduce labor while maintaining yield and quality are essential. This is primarily accomplished by reducing plant touches and matching pruning/training techniques to planting densities:
- The fewer plant touches, the less labor and the less opportunity for transfer of disease and pathogens. A good target for most indoor facilities is plant touches at cloning, planting, pruning, defoliation, and harvest. When performed correctly and at the appropriate times, a single plant touch for each of these stages is all that is required.
- In terms of pruning and training techniques, often “less is more”. If the veg time relative to planting density is within a good range, minimal foliage and branches need to be removed, saving both labor and plant resources.
Conclusion
Using the framework and techniques mentioned above can both improve profitability and improve sustainability of the cultivation operation. Implementing lean manufacturing principles gives businesses the best chance of improving and adapting in an uncertain and competitive production environment.
Managing over 2500 ft.² of cultivation area? Click HERE to apply for a commercial account and access our commercial support and pricing.